Please check our Instructions to Authors and send your manuscripts to nifs.journal@gmail.com.
Project:DMEU/Обобщени мрежи: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Обобщени мрежи, ОМ (Generalized nets, GNs''' са средство за конструиране на адаптивни, гъвкави и структурирани модели на комплексни системи, в които протичат паралелни във времето процеси и са изградени от множество взаимодействащи си компоненти. Обобщените мрежи представляват значително разширение и обобщение на понятието [[мрежи на Петри]], както и на други [[разширения и модификации на мрежи на Петри]]. | '''Обобщени мрежи, ОМ (Generalized nets, GNs''' са средство за конструиране на адаптивни, гъвкави и структурирани модели на комплексни системи, в които протичат паралелни във времето процеси и са изградени от множество взаимодействащи си компоненти. Обобщените мрежи представляват значително разширение и обобщение на понятието [[мрежи на Петри]], както и на други [[разширения и модификации на мрежи на Петри]]. | ||
== Компоненти на | == Компоненти на Обобщена мрежа == | ||
[[Image:GN-transition-mxn.png|right|thumb|25oxp|Преход от ОМ с ''m'' входа и ''n'' изхода]] | [[Image:GN-transition-mxn.png|right|thumb|25oxp|Преход от ОМ с ''m'' входа и ''n'' изхода]] | ||
Обобщената мрежа е изградена от преходи | Обобщената мрежа е изградена от преходи. '''Преходът''' в контекста на [[обобщените мрежи]] е обект от статичната структура на мрежата, който съдържа условията за преминаването на ядрата от входните в изходните му позиции, скед като преходът се е активирал. is an object from the static structure of the net, which comprises the conditions of [[token]]s' transfer from the transition's input [[place]]s to its output places. | ||
When tokens enter the input place of a transition, it becomes ''potentially fireable'' and at the moment of their transfer towards the transition's output places, the transition is being ''fired''. | |||
The tokens' transfer through a transition is described by a [[Algorithm for transition functioning|special formal algorithm]]. | |||
* статична структура, | * статична структура, | ||
* динамична структура, | * динамична структура, | ||
Revision as of 05:21, 20 August 2011
Изследване на възможностите
за използване на Data Mining за управление на процеси в електронен университет
Data Mining in Electronic University
(DMEU) |
Обобщени мрежи, ОМ (Generalized nets, GNs са средство за конструиране на адаптивни, гъвкави и структурирани модели на комплексни системи, в които протичат паралелни във времето процеси и са изградени от множество взаимодействащи си компоненти. Обобщените мрежи представляват значително разширение и обобщение на понятието мрежи на Петри, както и на други разширения и модификации на мрежи на Петри.
Компоненти на Обобщена мрежа
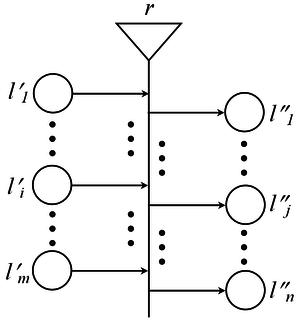
Обобщената мрежа е изградена от преходи. Преходът в контекста на обобщените мрежи е обект от статичната структура на мрежата, който съдържа условията за преминаването на ядрата от входните в изходните му позиции, скед като преходът се е активирал. is an object from the static structure of the net, which comprises the conditions of tokens' transfer from the transition's input places to its output places.
When tokens enter the input place of a transition, it becomes potentially fireable and at the moment of their transfer towards the transition's output places, the transition is being fired.
The tokens' transfer through a transition is described by a special formal algorithm.
- статична структура,
- динамична структура,
- temporal components.
The static structure consists of objects called transitions, which have input and output places. Two transitions can share a place, but every place can be an input of at most one transition and can be an output of at most one transition.
The dynamic structure consists of tokens, which act as information carriers and can occupy a single place at every moment of the GN execution. The tokens pass through the transition from one input to another output place; such an ordered pair of places is called transition arc. The tokens' movement is governed by conditions (predicates), contained in the predicate matrix of the transition.
The information carried by a token is contained in its characteristics, which can be viewed as an associative array of characteristic names and values. The values of the token characteristics change in time according to specific rules, called characteristic functions. Every place possesses at most one characteristic function, which assigns new characteristics to the incoming tokens. Apart from movement in the net and change of the characteristics, tokens can also split and merge in the places.
The temporal components describe the time scale of GN execution. Temporal conditions control the transitions' moments of activation and duration of active state. Various other tools for fine tuning of the GN functioning are provided in the form of priorities of separate transitions, places and tokens, as well as capacities of places and transitions arcs.
Graphic representation
Formal description
Formally described, the generalized net is represented by the following four-tuple:
where:
- 1. Static structure
- [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] is a set of transitions (see the formal definition of a transition)
- [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{A} }[/math] is a function giving the priorities of the transitions, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{A} : A \rightarrow N }[/math] where N = {0, 1, 2, ...} ∪ {∞}
- [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{L} }[/math] is a function giving the priorities of the places, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{L} : L \rightarrow N }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ c }[/math] is a function giving the place capacities, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ c : L \rightarrow N }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math] is a function giving the truth value of the predicates. In the basic case, it may obtain values "true" (1) and "false" (0). In fuzzy generalized nets its domain is the [0;1] interval (see fuzzy set) and in the intuitionistic fuzzy generalized nets its domain is the set [0;1]×[0;1] (see intuitionistic fuzzy set).
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{1} }[/math] is a function giving the next time moment when a given transition will be fired (will become active). Hence, [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{1}(t) = t' }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ t, t' \in [T, T+t^*]; t \le t' }[/math]. The value of this function is being recalculated in the moment when the transition's active state ceases.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{2} }[/math] is a function giving the duration of the transition's active state. Hence, [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_{2}(t) = t' }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ t, t' \in [T, T+t^*]; t' \ge 0 }[/math]. The value of this function is calculated in the moment when the transition's active state begins.
- 2. Dynamic structure
- [math]\displaystyle{ K }[/math] is the set of tokens of the generalized net. In certain cases it is more convenient to denote this set as [math]\displaystyle{ K = \bigcup_{l \in Q^I} K_{l} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ K_{l} }[/math] is the set of all GN tokens which are waiting to enter place [math]\displaystyle{ l }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ Q^I }[/math] is the set of all input places in the net.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_K }[/math] is a function giving the priorities of the tokens, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \pi_{K} : K \rightarrow N }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_K }[/math] is a function giving the moment of time when a given token may enter the GN, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ \theta_K (\alpha)=t }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha \in K, t \in [T; T+t^*] }[/math]
- 3. Time
- [math]\displaystyle{ T }[/math] is the moment of time when the generalized net starts functioning. This moment is determined according to a fixed global timescale.
- [math]\displaystyle{ t^0 }[/math] is the elementary time step of the fixed global timescale (the interval with which time increments in the timescale).
- [math]\displaystyle{ t^* }[/math] is the total duration of functioning of the net.
- 4. Memory
- [math]\displaystyle{ X }[/math] is the set of initial characteristics, which tokens may exhibit when they enter the net for first.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Phi }[/math] is a characteristic function, which assigns a new characteristic to each token when it makes the transfer from an input to an output place of a given transition.
- [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] is a function giving the maximal number of characteristics, which a given token may obtain during its movement throughout the net, i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ b : K \rightarrow N }[/math]. In general, [math]\displaystyle{ b }[/math] may possess four different values: 0, 1, [math]\displaystyle{ s }[/math] or [math]\displaystyle{ \infty }[/math] meaning that the token keeps, respectively: none of its characteristics, its last characteristic, its last [math]\displaystyle{ s }[/math] characteristics, or all of its characteristics obtained during its movement in the net.