Please check our Instructions to Authors and send your manuscripts to nifs.journal@gmail.com.
Necessity and possibility
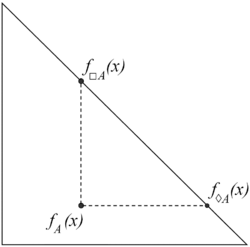
Necessity and possibility in the context of intuitionistic fuzzy sets are two modal operators defined as follows:
Let [math]\displaystyle{ E }[/math] be a fixed universe and [math]\displaystyle{ A \subset E }[/math] be a given set. Let functions [math]\displaystyle{ \mu_A, \nu_A \ : \ E \ \rightarrow [0,1] }[/math] determine the degrees of membership and non-membership. Then,
[math]\displaystyle{ \Box A = \lbrace \langle x, \mu_A(x), 1 - \mu_A(x) \rbrace \ | \ x \in E \rbrace }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Diamond A = \lbrace \langle x, 1 - \nu_A(x), \nu_A(x) \rbrace \ | \ x \in E \rbrace }[/math]
are called, respectively, necessity and possibility.
When [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] is a proper IFS, i.e. there exists an element [math]\displaystyle{ x \in E }[/math] for which [math]\displaystyle{ \mu_A(x) \gt 0 }[/math], then
[math]\displaystyle{ \Box A \subset A \subset \Diamond A }[/math]
[math]\displaystyle{ \Box A \ne A \ne \Diamond A }[/math].
Obviously, for every fuzzy set, i.e. intuitionistic fuzzy set with [math]\displaystyle{ (\forall x \in E)(\pi_A(x) = 0) }[/math] it holds that
[math]\displaystyle{ \Box A = A = \Diamond A }[/math].
Propositions about necessity and possibility
For every intuitionistic fuzzy set the following statements are valid:[1]
Proof of the first statement:
The following statements are also valid:[2]
References
- ↑ Proposition 1.42, page 61 from Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets: Theory and Applications, Krassimir Atanassov, Springer, 1999.
- ↑ Theorem 1.43, page 62 from Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets: Theory and Applications, Krassimir Atanassov, Springer, 1999.